B型肝炎病毒
What is it?
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection that causes inflammation (swelling and reddening) that can lead to liver damage. Hepatitis B, also called HBV and Hep B, can cause cirrhosis (hardening or scarring), liver cancer and even death.
What are the symptoms of hepatitis B?
- Achy muscles or joints.
- Stomach pain.
- Loss of appetite.
- Mild fever.
- Loose stool (diarrhea).
- Lack of energy.
- Constipation.
- Having yellow skin or eyes (jaundice).
- Being sick to your stomach.
- Brown urine.

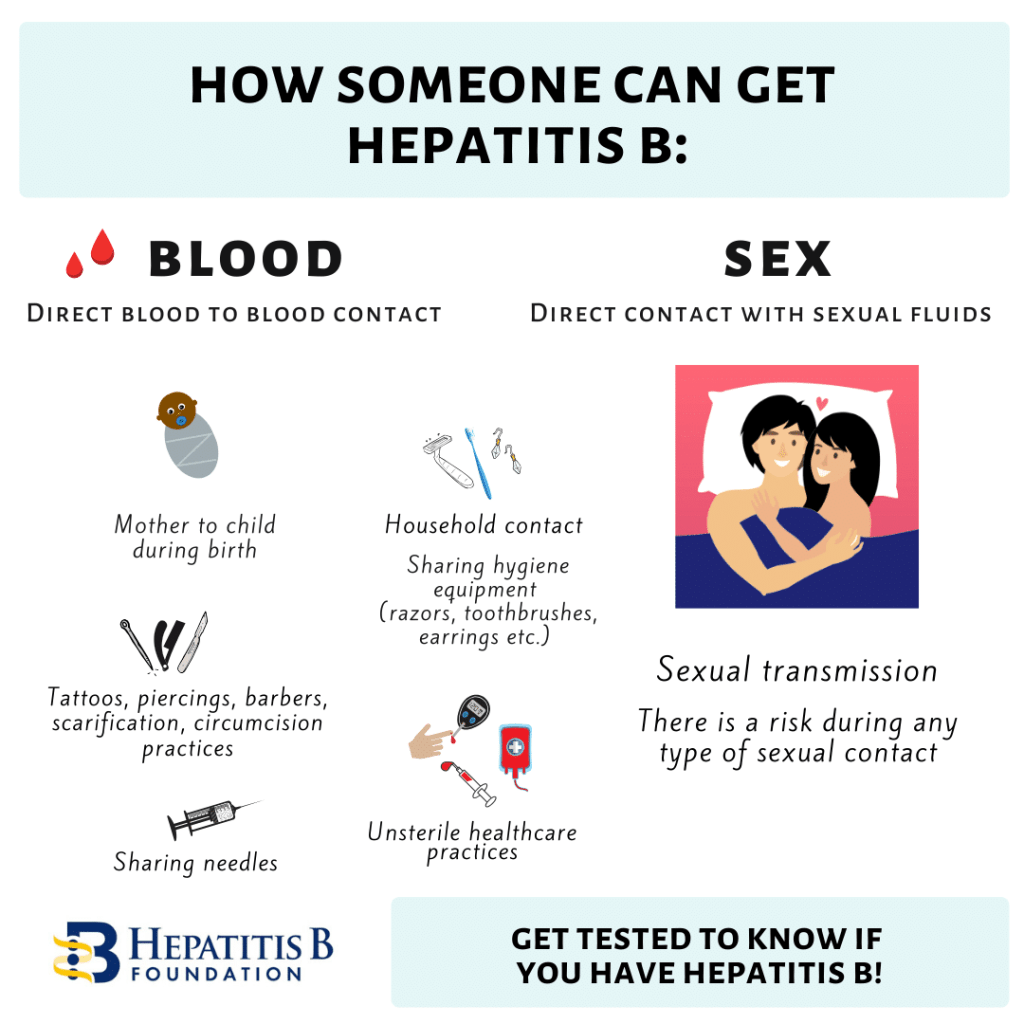
How is hepatitis B spread?
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.

Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
- Breastfeeding.
Who are risk getting Hepatitis B?
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.

How do we check for Hepatitis B infection?
- Blood tests
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Liver biopsy
What are the long-term effects of hepatitis B?
The long-term complications of hepatitis B may include:
- Becoming a hepatitis B carrier.
- Chronic hepatitis B infection.
- Cirrhosis (scarring of the liver).
- Liver cancer.
- Liver failure.
- Death
Take home message
Patient with hepatitis B should consult a specialist doctor every 6 months to 1 year for monitoring 🙂
Leave a comment